Services
Find a Location

Hearing Aid Evaluations

Hearing Aid Fittings

Custom Hearing Protection

Assistive Listening Devices
Assistive Listening Devices (ALDs) are an important tool for people with hearing impairments. They provide a way to amplify sound and make it easier to understand speech in noisy environments. ALDs can also be used to help people with hearing impairments communicate better in social situations and make sure that they don’t miss out on important conversations. ALDs come in a variety of shapes and sizes, from personal amplifiers that fit into the ear canal, to devices that can be worn around the neck or clipped onto clothing.
Contact Us

Sound Sensitivity and Misophonia
Contact Us
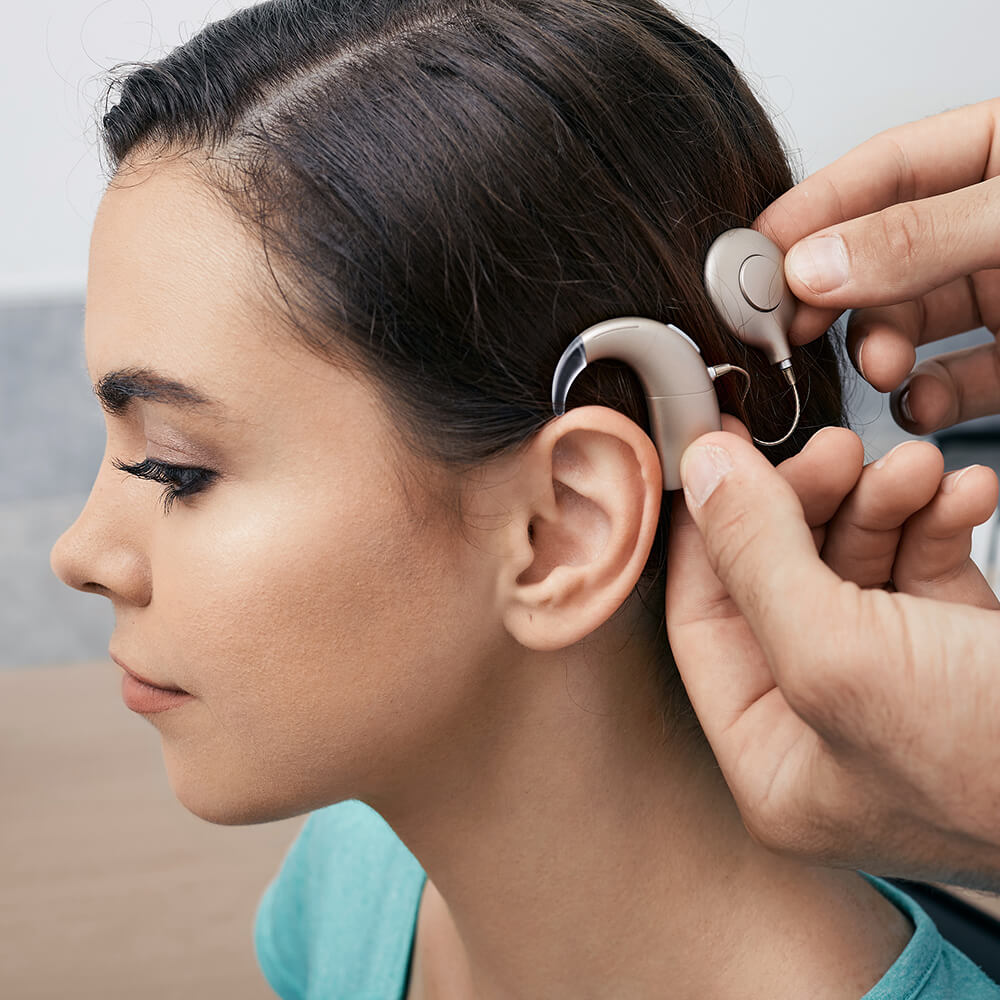

Cochlear Implants and Bone Anchored Hearing Aids
Contact Us
Concussion and TBI Testing
Contact Us

